CASE STUDY
Building the Tokyo Digital Twin with TerriaJS and Cesium ion
Tokyo, a metropolis of around 14 million people, constantly evolving, faced a monumental task: how to unify its sprawling urban information into a single, understandable view. The answer came in the form of an advanced, interactive geospatial platform, known as the Tokyo Digital Twin. This wasn't just about mapping streets; it was about building a dynamic, real-time reflection of the city, empowering officials and citizens alike.
Key takeaways
Need: Unify sprawling urban information from multiple Tokyo government departments into a single, understandable view.
Solution: Comprehensive digital twin platform combining TerriaJS's open-source flexibility with Cesium ion's 3D visualisation capabilities to create an immersive, real-time reflection of Tokyo.
Technology: Integration of real-time sensor data, BIM models, 3D tiles, disaster simulation outputs, and open government datasets within TerriaJS's modular, web-based platform with seamless 2D/3D switching and bilingual accessibility.
Improved crisis simulation and disaster response planning capabilities
Enhanced citizen engagement through intuitive neighbourhood risk visualisation
Streamlined cross-departmental collaboration with unified data sharing
Tokyo Digital Twin Project presentation at the Cesium Developer Conference, June 2025
Goals and vision
The visionary team at Pacific Spatial Solutions and Mitsubishi Research Institute working in close collaboration with the Tokyo Metropolitan Government, embarked on this ambitious journey. They chose TerriaJS and Cesium ion, a powerful combination of technologies, to be the bedrock of a project that would redefine urban planning and disaster preparedness.
Through the Tokyo Digital Twin Program, The Tokyo Metropolitan Government initiated the Digital Twin project with the following primary objectives:
Visualize complex urban data from various departments in an integrated 3D environment.
Support disaster preparedness and response planning, particularly for earthquakes and floods.
Enhance transparency and collaboration with the public and private sectors through open data.
Accelerate smart city initiatives by providing a platform for urban simulation and scenario planning
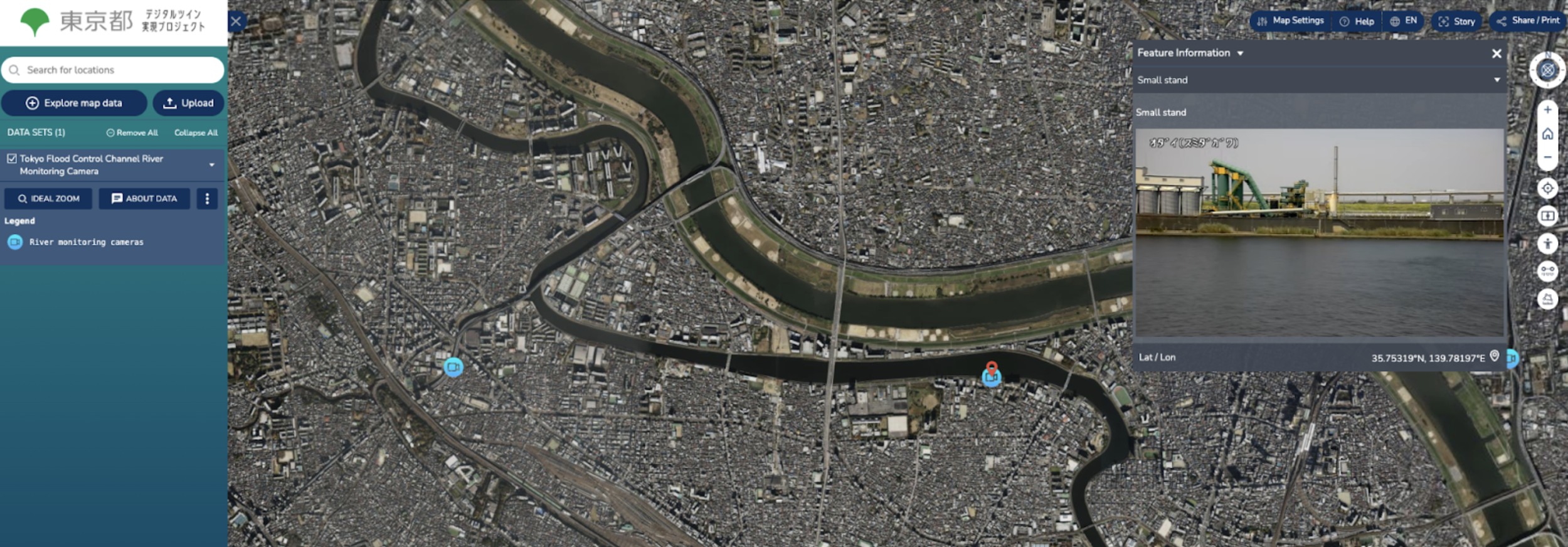
Tokyo Flood Control Channel River monitoring camera (live capture)
Why TerriaJS?
TerriaJS is open-source, which provided Tokyo with unparalleled control and freedom to customize the platform to its specific needs, a crucial advantage in a project of this scale. TerriaJS's robust 3D visualization capabilities, seamlessly integrating with Cesium ion for stunning terrain and building models, were essential for creating an immersive and accurate representation of the city.
The platform’s flexibility in handling diverse data formats – from WMS and WFS to 3D tiles, GeoJSON and live data streams – meant that no valuable dataset would be left behind. Crucially, its ease of integration with existing government data portals and GIS workflows ensured rapid deployment, enhancing Tokyo’s existing investments and capabilities.
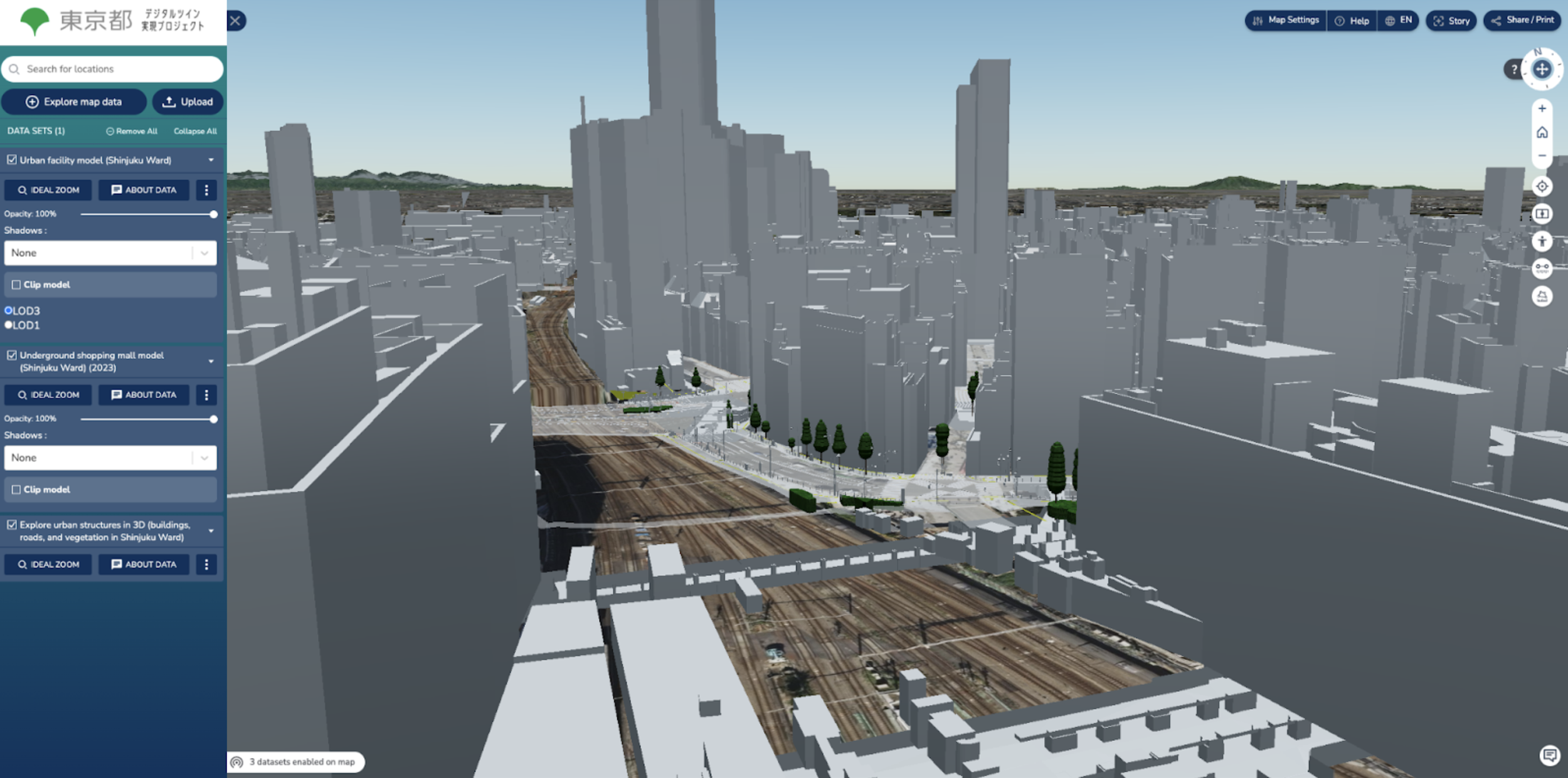
Integration of vegetation, buildings and underground data for Shinjuku Ward
Implementation highlights
Data integration
Tokyo’s digital twin integrates datasets from many sources:
Real-time sensor data (e.g., weather, traffic)
BIM and 3D urban models
Disaster simulation outputs (e.g., flood zones, seismic intensity)
Open data from city planning, infrastructure, and demographics
These datasets are layered in a coherent geospatial interface that allows users to toggle visibility, filter information, and query specific regions.
3D visualisation
TerriaJS, combined with Cesium ION, enabled the development of an immersive 3D representation of Tokyo:
Buildings are visualized in detail using 3D tiles.
Simulation overlays (e.g., tsunami inundation) appear directly over the terrain.
Users can switch between 2D and 3D views seamlessly.
It brings together the three key ingredients of a spatial digital twin: the built environment, the natural environment and live data.
User experience and accessibility
Recognising the diverse audience, from urban planners to everyday citizens, the user experience was crafted for intuition and accessibility. A responsive design ensured seamless functionality on both desktop and mobile devices. Bilingual support in Japanese and English bridged language barriers, while searchable location indexes and thematic maps offered quick access to vital insights.
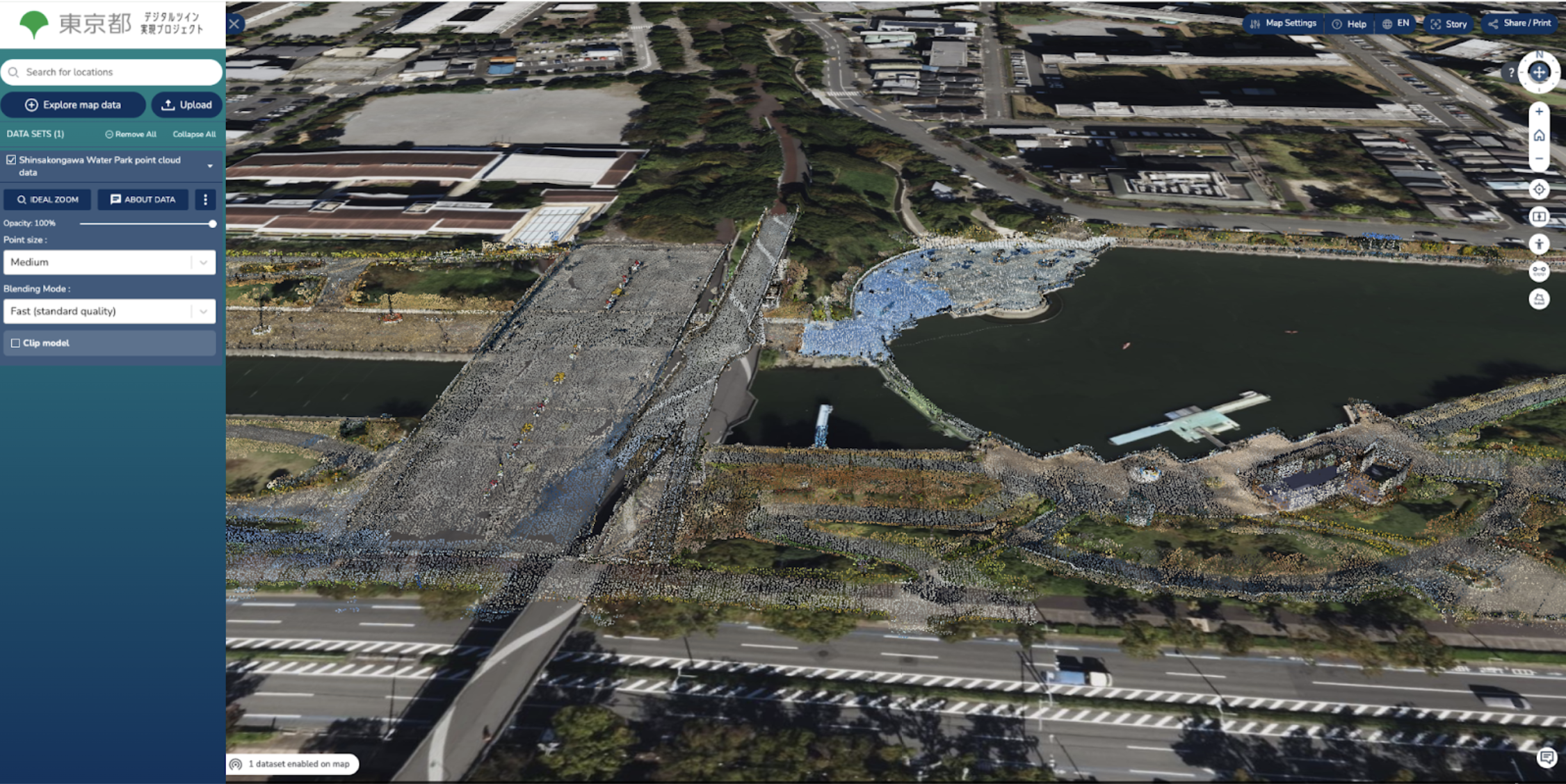
Shinsakongawa Water Park point cloud, Industry-Academia-Government FY 2022 data collaboration demonstration
Outcomes and impact
The Tokyo Digital Twin has already demonstrated several key benefits:
Increased preparedness: Authorities use the tool for crisis simulations and risk communication.
Enhanced public engagement and trust: Citizens explore their neighbourhoods and understand risks through the web interface.
Cross-agency collaboration: City departments share consistent data layers, breaking down silos and duplication.
Lessons learned
Reflecting on this transformative project, several key lessons emerged.
The modular architecture of TerriaJS, with its plugin-based structure, proved invaluable, allowing the project team to rapidly iterate and integrate new features as needs evolved.
The power of open data was undeniable; by leveraging publicly available datasets, the project avoided expensive vendor lock-in and paved the way for broader use and a higher return on investment.
And finally, the importance of visual clarity shone through. Terria's user-friendly storytelling and layering features made complex data digestible and accessible to diverse audiences, driving widespread adoption and engagement.
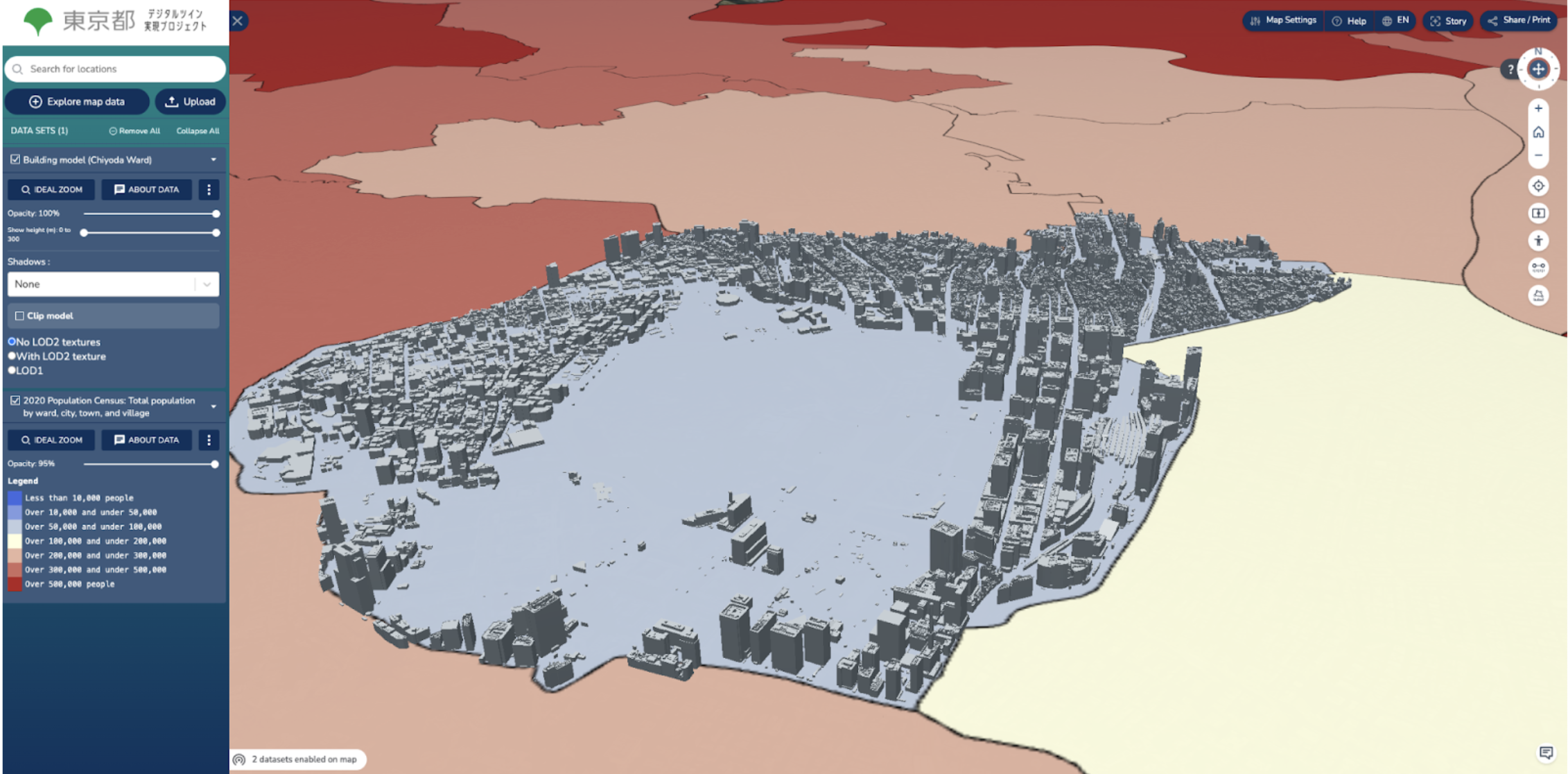
Integration of population information and buildings data for Chiyoda Ward
The Tokyo Digital Twin is a model example of using TerriaJS and Cesium ion to build scalable, open, and interactive urban platforms. It proves how modern geospatial tools can transform complex data into actionable insight, fostering smarter and more resilient cities.

Take your spatial project to the next dimension
See how teams like yours are building digital twins that engage stakeholders and accelerate decisions.